Quick links: MarkVCID1 Framework & Protocols MarkVCID1 Data Access MarkVCID1 Biomarker Kits
MarkVCID1 Validation Results
The goal of the first phase of the MarkVCID consortium (MarkVCID1) was to perform validation studies on a selected group of neuroimaging- and fluid-based candidate biomarkers for cerebral small vessel disease. In coordination with the NINDS and an external advisory board, the MarkVCID1 consortium selected 11 of 36 proposed biomarker kits for multi-site validation. Details on the six MRI-based candidates (WMH, PSMD, FW, ARTS, CVR, and WMH-G/R), one OCTA-based candidate (OCTA-VSD), and four fluid-based candidates (NfL, EGF, ExE, and CSF-PlGF) are available below.
The consortium designed and implemented rigorous validation protocols for assessing each biomarker kit’s instrumental validity (inter-rater reliability for imaging biomarkers/interplate repeatability for biofluid biomarkers, test-retest repeatability, and inter-site reproducibility) and biological validity (association with clinical measures of cognitive function in a minimum of three independent patient cohorts). See definitions and related manuscripts below for details.
The tables below present summaries of the instrumental and biological validation results from the 11 candidate biomarker kits. The clinical measures of cognition used for biological validation were chosen individually by the biomarker’s lead investigators.
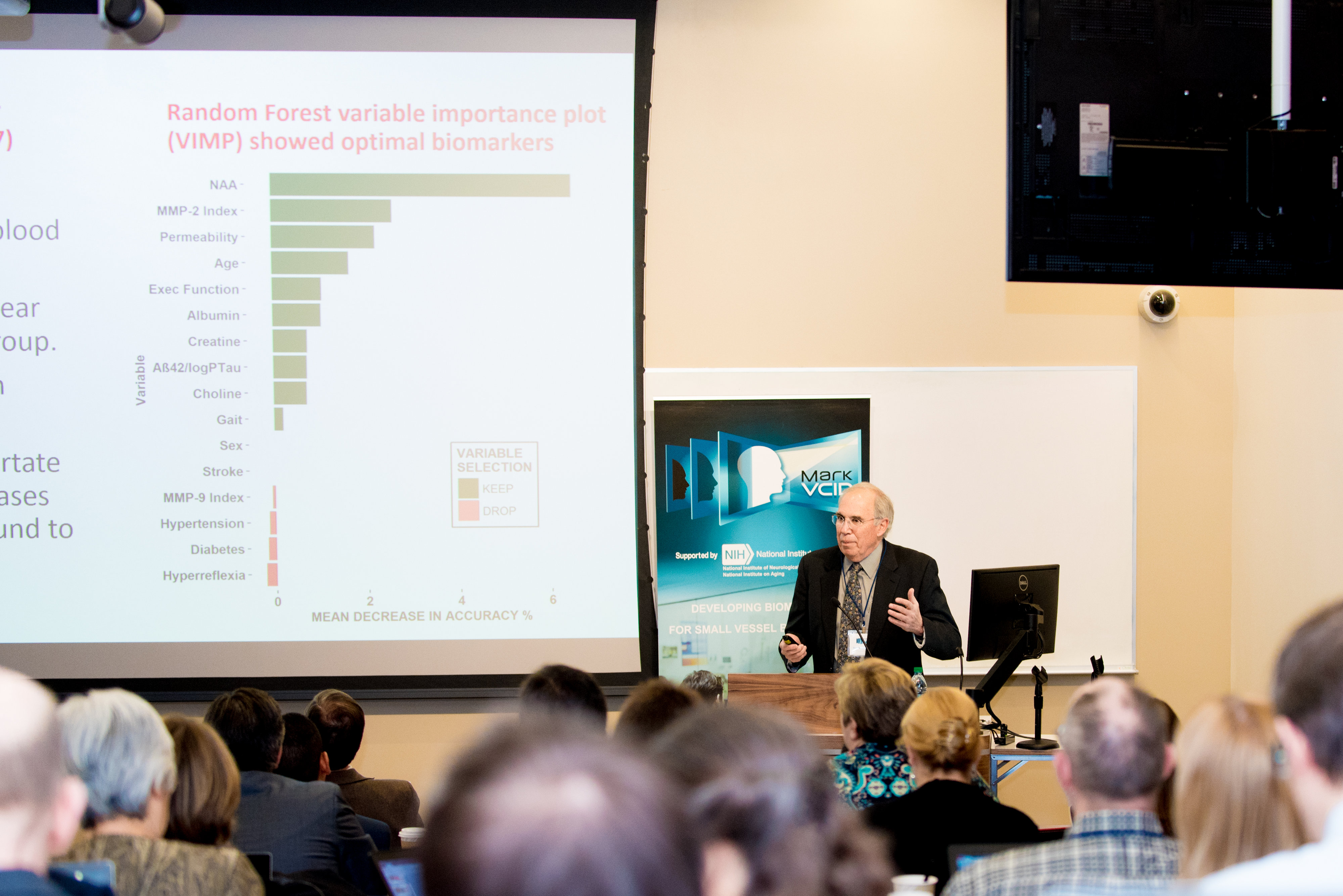
As shown below, the imaging-based biomarker kits demonstrates robust instrumental reliability. Key findings include high inter-rater reliability and test-retest repeatability, particularly for ARTS, WMH, FW, and PSMD. Inter-scanner reproducibility was also high for all MRI-based biomarkers. In the biological validation step, strong associations with the different cognitive function measures were observed in multiple independent prospective and legacy cohorts.
The evaluation of fluid-based biomarker kits revealed moderately high instrumental reliability and variable associations with cognitive function in biological validation. Plasma NfL demonstrated high instrumental reliability (interplate repeatability, test-retest reliability, and inter-site reproducibility) and strong biological associations to cognitive performance. CSF PlGF showed good interplate repeatability and inter-site reliability, while Plasma EGF and Plasma ExE demonstrated more variability and less instrumental reliability. NfL demonstrated significant association with generalized cognitive function in the biological validation step. While EGF and ExE are linked to executive function composites, the evidence is less robust, with ExE requiring further validation.
In summary, a subset of the biomarkers tested in MarkVCID1 have shown promise for potential application in clinical trial settings. These results supported further clinical validation of selected MarkVCID1 biomarkers in the consortium’s MarkVCID2 phase.
Click on the biomarker name for more information.
Definitions
1 Instrumental validation
Imaging instrumental validation is operationally defined as:
- Inter-rater reliability (differences between values obtained for MRI biomarkers from different sites analyzing the same MRI data)
- Test-retest repeatability (differences between results for MRI biomarkers obtained using scans of the same individual obtained on the same MRI scanner either on different days OR on the same day separated by a short time interval)
- Inter-site reproducibility (differences between results for MRI biomarkers using scans of the same individual obtained on different MRI scanners). See Neuroimaging Protocols manuscript below for more details.
Fluid-based biomarkers instrumental validation is operationally defined as:
- Intra- and inter-plate repeatability (repeat assays of single split fluid samples performed at individual sites)
- Test-retest repeatability (assay of three samples acquired from the same individual, collected at least 5 days apart over a 30-day period and assayed on a single plate)
- Inter-site reproducibility (assays of split samples distributed to multiple sites)
2 Biological validation
Both imaging and fluid-based biomarker kits were assessed for their association with clinically meaningful aspects of VCID such as cognitive and functional performance either cross sectionally or longitudinally.
3 Independent site validation
The investigator utilized data and/or samples from at least three independent institutions that each met the necessary sample size for biomarker kit validation.
4 Legacy cohorts
The investigator utilized data and/or samples from existing cohorts including Rush MAP study, CHARGE studies, and ADRCs from UCD, UCSF, and UKY.
5 Pooled site validation
The investigator combined data and/or samples from at least three institutions to meet the necessary sample size for the biomarker kit validation.



Companion manuscripts published by Alzheimer's & dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association (Apr 2021):
I. Enrollment, clinical, fluid protocols (https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12215)
II. Neuroimaging protocols (https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12216)
Key features of MarkVCID1 participant enrollment, clinical/cognitive testing, fluid biomarker procedures, and imaging biomarker procedures are described in the papers above. The protocols address a range of goals in MarkVCID's study design, notably:
- Acquiring all data under informed consent and enrollment procedures that allow unlimited sharing and open-ended analyses without compromising participant privacy rights;
- Acquiring the data in a sufficiently wide range of study participants to allow assessment of candidate biomarkers across the various patient groups who might ultimately be targeted in VCID clinical trials;
- Defining a common dataset of clinical and cognitive elements that contains all the key outcome markers and covariates for VCID studies and is realistically obtainable during a practical study visit;
- Instituting best fluid-handling practices for minimizing avoidable sources of variability; and
- Establishing rigorous procedures for testing the reliability of candidate imaging and fluid-based biomarkers
See MarkVCID1 Biomarker Protocols and Study Resources (https://markvcid.partners.org/markvcid1-protocols-resources)



To request deidentified MarkVCID1 imaging, clinical/cog data, and/or biosamples, see “Search Data”
At the completion of MarkVCID1, the consortium had collectively enrolled 653 participants across six research sites and achieved 90% longitudinal participant retention (defined as at least one follow-up visit) despite challenges faced during COVID-19.
MarkVCID research is openly shared both within and outside the MarkVCID consortium to the greatest extent practical. As per the MarkVCID Consortium’s Charter, MarkVCID investigators are granted broad access to MarkVCID data, samples, analytic tools, and other resources with relevant permissions in place. Collaborators agree not to sell participant biosamples or data for profit. However, any scientific knowledge gained from the biosamples and/or data may be used in the future to develop products that could be used for profit. Publications resulting from the use of MarkVCID data are expected to acknowledge the MarkVCID consortium as outlined in the MarkVCID Data Use and Publications Policy (see Sharing & Publications dropdown menu).
Groundwork for MarkVCID2
The NINDS and external advisors selected five of the eleven MarkVCID1 biomarker kits to undergo clinical validation in MarkVCID2: MRI-based Peak Skeletonized Mean Diffusivity (PSMD), Free Water (FW), ARTS, and Cerebrovascular Reactivity (CVR); and fluid-based Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain (NfL). In addition to the primary biomarkers, investigators will also consider combinations including NfL and FW; PSMD and NfL; and ARTS, FW and NfL.
To read more about MarkVCID2 click here.



Kit lead: Charles DeCarli, MD (UCD/UCSF)
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
WMH will associate with measures of processing speed (Trails B-A and IRT specific executive function measure) - Primary context of use: Selection of subjects for enriched vascular disease
- Primary biomarker category: Stratification variable to enrich study populations for vascular disease
- Participating sites: JHU, UCSF/UCD, UKY, UNM, USC, UTHSCSA
- Sample size: 104
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
MRI WMH Volume Protocol (v2_1.17.19)
- Supporting Documents:

Kit lead : Claudia Satizabal, PhD, UTHSCSA & CHARGE
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Higher PSMD will be associated with poorer general cognitive function in dementia-free participants
- Primary context of use: To stratify high risk individuals for inclusion VCID trials
- Primary biomarker category: Susceptibility/Risk
- Participating sites: Biological validation: CHARGE, UCD/UCSF, Rush, combined UH3 sites [UKY, UNM, USC, UTHSCSA] Instrumental validation: UTHSA, UKY, UCSF, UNM, JHU, USC, Rush
- Sample size: 175
Biomarker kit protocol & resources

Kit leads: Pauline Maillard, PhD (UCD) & Arvind Caprihan, MD (UNM)
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Higher baseline mean white matter free water fraction (mFW) values will be associated with lower baseline executive function composite (EFC) score.
- Primary context of use: Early identification of VCID subjects at risk for cognitive decline for inclusion in trials
- Primary biomarker category: Susceptibility/Risk
- Participating sites: JHU, UCSF, UKY, UNM, USC, UTHSCSA
- Sample size: 123
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
MRI Free Water Kit Protocol (v6.12.23)
- Supporting Documents:

Kit lead: Konstantinos Arfanakis, PhD, Rush University
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Primary prespecified hypothesis: Biomarker score is associated with faster cognitive decline two years after MRI. - Primary context of use: Primary context of use: The higher the score, the higher the likelihood of arteriolosclerosis and therefore the higher the risk of cognitive decline.
- Primary biomarker category: Susceptibility/Risk
- Participating sites:
- Biological validation: Rush-IIT, UKY, CHARGE (ARIC Study)
- Instrumental validation: UTHSCSA, UNM, UKY, UCSF, UNM, JHU, USC
- Minimum sample size: 120
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
MRI ARTS Kit Protocol (v7.13.23)
- Supporting documents:


Kit lead: Hanzhang Lu, PhD, JHU
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Whole-brain CVR is associated with Montreal Cognitive Assessment for Dementia (MoCA) score after adjusting for age, sex, and education - Primary context of use:
Primary context of use: To stratify patients for clinical trial based on probability to progress to dementia - Primary biomarker category: Susceptibility/Risk
- Participating sites: UTHSCSA, USC, UKY, UNM
- Sample size: 75
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
Supporting Documents:


Kit leads: Greg Jicha, MD, PhD & Ahmed Bahrani, PhD
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Growth will correlate with supraspan word list delayed free recall Z-scores - Primary context of use:
Isolate growth/regression as unique variables depending on proposed mechanism of action - Primary biomarker category: Disease Progression
- Participating sites: USC, JHU, UTHSCSA, UNM, UCSF/UCD, Rush legacy cohort
- Sample size: 175
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
MRI WMH Growth/Regression Kit Protocol (v.3.31.20)
Supporting Documents:
- Longitudinal WMH Protocol Container Instructions (v.2022)
- WMH Growth/Regression Recorded Webinar (v.7.24.20)


Kit lead: Amir Kashani, MD, PhD (USC/JHU)
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
Determine the odds of cognitive impairment corresponding to a retinal vessel skeleton density (VSD) measurement. The primary outcome variable of cognitive impairment will be MoCA. - Primary context of use:
Susceptibility biomarker to enrich for enrollment of subjects with significant contribution of cerebral small vessel disease to development of cognitive impairment and dementia
- Primary biomarker category: Susceptibility/Risk
- Participating sites:
- Biological validation: UCSF, JHU, UTHSCSA, USC, Rush
- Sample size: 60
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
OCTA VSD Kit Protocol (v6.11.20)
- Supporting Documents:
- Lower retinal capillary density in minimal cognitive impairment among older Latinx adults
A&D Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring (Aug 2020) - MarkVCID OCTA Acquisition Instructions (v.1.16.21)
- MarkVCID OCTA Centration Guide (v12.7.20)
- VSD Biomarker Kit Analysis Software (v.4.21.20)
- Device Cleaning Instructions
- Lower retinal capillary density in minimal cognitive impairment among older Latinx adults
Related Required Trainings

Kit leads: Sudha Seshadri, MD & Claudia Satizabal, PhD, UTHSCSA & CHARGE
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis: Elevated concentrations of NfL will be related to lower cognitive function
- Primary context of use: Risk stratification for enrollment in clinical trials
- Primary biomarker category: Susceptibly/Risk
- Participating sites:
- Instrumental validation: UTHSA, UKY, USC, UNM, JHU, UCSF
- Biological validation: UCD ADRC, UKY ADRC, CHARGE, MarkVCID (USC+UNM+JHU+UKY+UCD+UCSF+UTHSCSA)
on Quanterix HD-1/HD-X instruments
- Sample size: 330
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
- Plasma NfL Kit Protocol (v10.30.19)
(Note neuro 4-plex A kit will be discontinued in 2025) - MarkVCID NfL Lab Protocol and Instrumental Validation (v.3.5.20)
- Plasma & Serum Sample Clarification - UVM Procedure (v.3.5.20)

Kit leads: Jason Hinman, MD, PhD, UCSF/UCLA; Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD UCSF/Mt. Sinai
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
An equally-weighted, normalized, population mean adjusted composite of three endothelial signaling molecules (VEGF-D, PlGF, bFGF) associate with increased cognitive impairment measured by CDR - Primary context of use: Subject selection
- Primary biomarker category: Risk Stratification
- Participating sites: UNM, UKY, UCLA, UVM (CHARGE)
- Sample size: 96
Biomarker kit protocol & resources

Kit lead: Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD, UCSF/Mt. Sinai
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
(1) EDE complement factors (Endothelial-derived exosomal C3b and C1q) are higher in subjects with cerebral small vessel disease than those without (2) Levels of EDE-C are associated with Executive Function (IRT) - Primary context of use: Subject selection
- Primary biomarker category: Diagnostic classification
- Participating sites:
- UVM (CHARGE), UCD, UCSF
- Sample size: 45
- Sample type: Platelet-poor plasma
- Assay: EDE isolation 🡪 colorimetric ELISA
Biomarker kit protocol & resources
Plasma Exosome Endothelial Inflammation Kit Protocol (v10.28.19)
- Supporting Documents:

Kit lead: Donna Wilcock, PhD (UKY/IU)
Biomarker kit overview
- Primary prespecified hypothesis:
CSF PlGF levels, assessed by Quanterix Simoa assay, will be associated with white matter hyperintensity volume and TRAILS-A cognitive assessment. - Primary context of use: Clinical trial stratification to determine presence of SVD. Can be used alongside CSF Abeta, tau, NfL to stratify AD / VCID / both.
- Primary biomarker category: Disease Stratification
- Participating sites: UTHSCSA, UCSF, JHU
- Sample size: 40 CSF samples with MRI & clinical assessments
Biomarker kit protocol & resources








